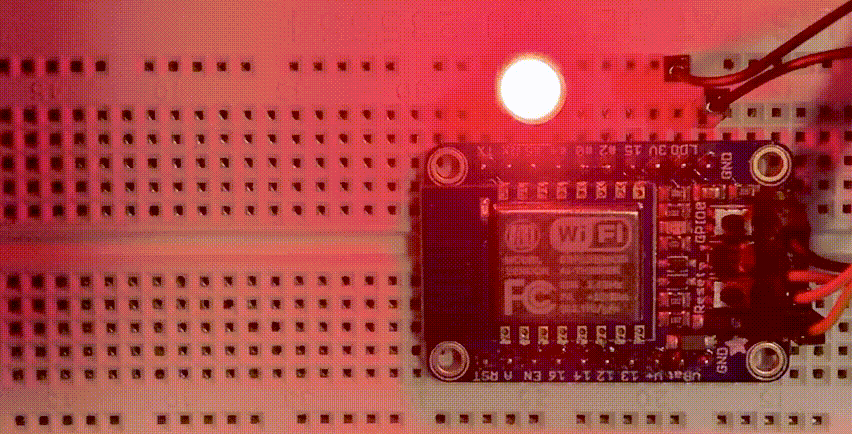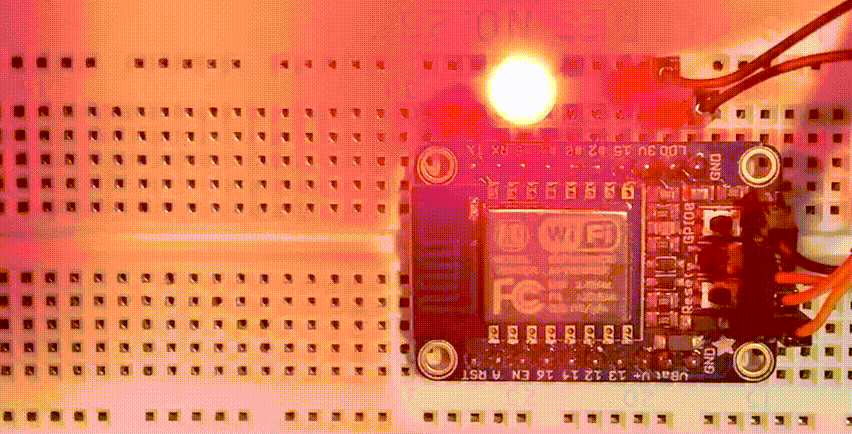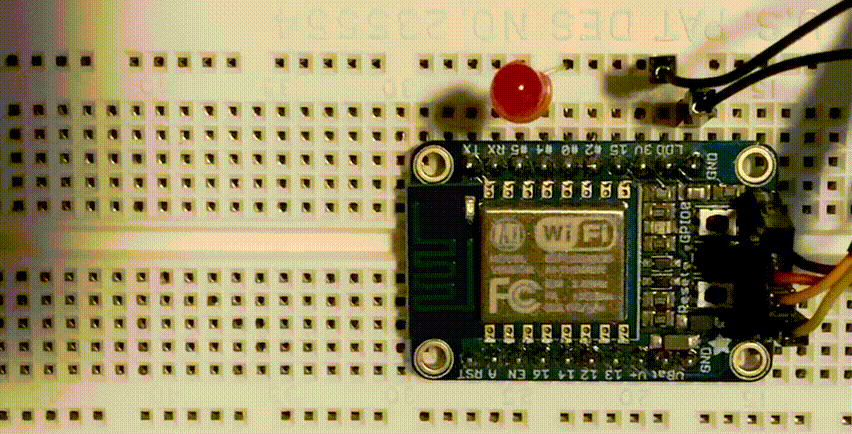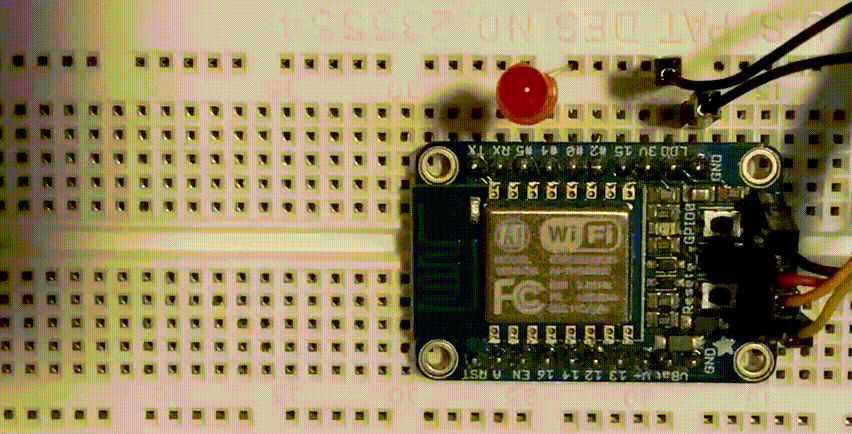
The ESP8266 is a low cost 80 MHz microcontroller with a full WiFi support. It can be found on several breakout boards, with Adafruit’s HUZZAH ESP8266 being one of the better ones. For about $10 you can own a small internet connected microcontroller that can be programmed in MicroPython.
ESP8266
- 64 KB of instruction RAM
- 96 KB of data RAM
- 4 MB of FLASH Memory
Breakout Board
- 1 x Analog input (1.0V max)
- 9 x GPIO (3.3V logic), which can also be used for I2C or SPI
- 2 x UART pins
- 2 x 3-6V power inputs, reset, enable, LDO-disable, 3.3V output
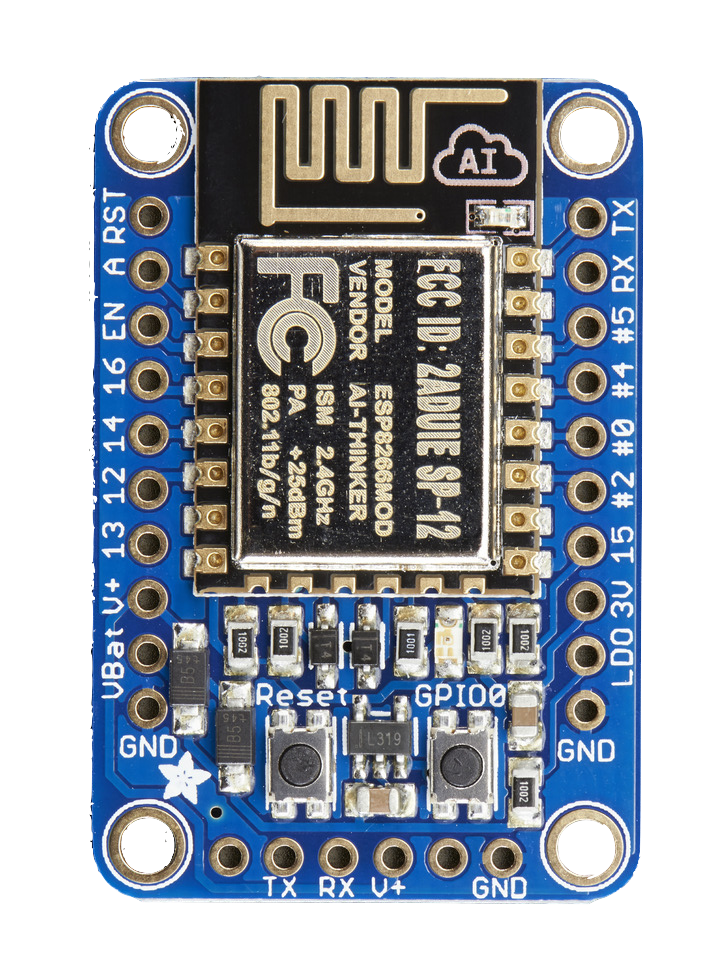
GPIO and Power Levels
RX and TX (aka GPIO1 and GPIO3) are the serial control and bootloading pins and can be found on the right side as well as on the bottom of the board.
RX and V+ are the only 5V compliant pins. TX, the output from the module and is 3.3V logic. All GPIO pins are 3.3V in and out, and are not 5V compatible.
The Analog Pin (A, top left), has a 1.0V maximum voltage.
Micro Python
MicroPython is a tiny open source Python programming language interpreter that runs on small embedded development boards.
Get started by installing Python3, and then pip-install esptool and adafruit-ampy:
pip3 install esptool --upgrade pip3 install adafruit-ampy --upgrade
The breakout board does not provide a usb socket, a USB to TTL Serial Cable is needed to communicate with the device. Using such a cable with a FTDI chip comes with the advantage that drivers are preinstalled on macOS (even when using an Apple-Silicon based Mac).
Flashing Micro Python on the ESP8266
With an USB to Serial Cable attached to the Mac and the ESP8266 Breakout Board, the ESP needs to be put into “Boot-loading Mode”. For that to happen, press and hold the GPIO button (button on the right) and then press and release the Reset button (button on the left). The red LED between those two buttons should be on now but dim.
Once the device is in boot-loading mode, start with erasing the flash memory:
esptool.py --port /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO erase_flash
esptool.py v4.3 Serial port /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO Connecting... Detecting chip type... Unsupported detection protocol, switching and trying again... Connecting... Detecting chip type... ESP8266 Chip is ESP8266EX Features: WiFi Crystal is 26MHz MAC: 18:fe:34:fe:a3:ba Stub is already running. No upload is necessary. Erasing flash (this may take a while)... Chip erase completed successfully in 0.0s Hard resetting via RTS pin...
Download the latest stabile MicroPython Firmware for ESP8266 with more than 2MB Espressif boards: (currently v1.19.1) and flash it onto the board:
esptool.py --port /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO --baud 115200 write_flash --flash_size=detect 0 ~/Downloads/esp8266.bin
esptool.py v4.3 Serial port /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO Connecting.... Detecting chip type... Unsupported detection protocol, switching and trying again... Connecting... Detecting chip type... ESP8266 Chip is ESP8266EX Features: WiFi Crystal is 26MHz MAC: 18:fe:34:fe:a3:ba Uploading stub... Running stub... Stub running... Configuring flash size... Auto-detected Flash size: 4MB Flash will be erased from 0x00000000 to 0x0009afff... Flash params set to 0x0040 Compressed 634844 bytes to 419808... Wrote 634844 bytes (419808 compressed) at 0x00000000 in 37.3 seconds (effective 136.1 kbit/s)... Hash of data verified. Leaving... Hard resetting via RTS pin...
After a reset,
screen /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO 115200
will show the python prompt and entering help(), will display the following output:
Welcome to MicroPython!
For online docs please visit http://docs.micropython.org/en/latest/esp8266/ .
For diagnostic information to include in bug reports execute 'import port_diag'.
Basic WiFi configuration:
import network
sta_if = network.WLAN(network.STA_IF); sta_if.active(True)
sta_if.scan() # Scan for available access points
sta_if.connect("", "") # Connect to an AP
sta_if.isconnected() # Check for successful connection
# Change name/password of ESP8266's AP:
ap_if = network.WLAN(network.AP_IF)
ap_if.config(essid="", authmode=network.AUTH_WPA_WPA2_PSK, password="")
Control commands:
CTRL-A -- on a blank line, enter raw REPL mode
CTRL-B -- on a blank line, enter normal REPL mode
CTRL-C -- interrupt a running program
CTRL-D -- on a blank line, do a soft reset of the board
CTRL-E -- on a blank line, enter paste mode
For further help on a specific object, type help(obj)
and CTRL-D shows the current OS version: E.g.,:
MPY: soft reboot MicroPython v1.19.1 on 2022-06-18; ESP module with ESP8266 Type "help()" for more information.
How much Memory?
>>> import gc >>> gc.collect() >>> gc.mem_free() 36512 >>>
.. gc.mem_free() returns the free heap size in bytes. Therefore, about 35 KBytes of Heap Memory is available.
Modules
>>> help('modules')
__main__ math ucollections ure
_boot micropython ucryptolib urequests
_onewire neopixel uctypes urllib/urequest
_uasyncio network uerrno uselect
_webrepl ntptime uhashlib usocket
apa102 onewire uheapq ussl
btree port_diag uio ustruct
builtins ssd1306 ujson usys
dht uarray umachine utime
ds18x20 uasyncio/__init__ umqtt/robust utimeq
esp uasyncio/core umqtt/simple uwebsocket
flashbdev uasyncio/event uos uzlib
framebuf uasyncio/funcs upip webrepl
gc uasyncio/lock upip_utarfile webrepl_setup
inisetup uasyncio/stream upysh websocket_helper
lwip ubinascii urandom
Plus any modules on the filesystem
Builtins
>>> import builtins >>> dir(builtins) ['__class__', '__name__', 'ArithmeticError', 'AssertionError', 'AttributeError', 'BaseException', 'EOFError', 'Ellipsis', 'Exception', 'GeneratorExit', 'ImportError', 'IndentationError', 'IndexError', 'KeyError', 'KeyboardInterrupt', 'LookupError', 'MemoryError', 'NameError', 'NotImplementedError', 'OSError', 'OverflowError', 'RuntimeError', 'StopIteration', 'SyntaxError', 'SystemExit', 'TypeError', 'ValueError', 'ZeroDivisionError', 'abs', 'all', 'any', 'bool', 'bytearray', 'bytes', 'callable', 'chr', 'classmethod', 'dict', 'dir', 'divmod', 'eval', 'exec', 'getattr', 'globals', 'hasattr', 'hash', 'id', 'int', 'isinstance', 'issubclass', 'iter', 'len', 'list', 'locals', 'map', 'next', 'object', 'open', 'ord', 'pow', 'print', 'range', 'repr', 'round', 'set', 'setattr', 'sorted', 'staticmethod', 'str', 'sum', 'super', 'tuple', 'type', 'zip', '__build_class__', '__import__', '__repl_print__', 'StopAsyncIteration', 'UnicodeError', 'ViperTypeError', 'bin', 'delattr', 'enumerate', 'filter', 'float', 'frozenset', 'help', 'hex', 'input', 'max', 'memoryview', 'min', 'oct', 'property', 'reversed', 'slice'] >>>
Blinky
Assuming that Wifi won’t work any different than on the ESP32, let’s blink an LED, connected to GPIO5 and GRN.
""" Blinky ESP8266 - main.py """ import time from machine import Pin p = Pin(5, Pin.OUT) state = True while True: p.value(state) state = not state time.sleep(1)
With adafruit-ampy installed, the main.py script can be deployed like so:
ampy --port /dev/tty.usbserial-A900gcOO put main.py